ERP aims to unify the entire business on a single, shared system. ERP can automate and reduce paper-based processes for a variety of commercial operations. It may schedule and monitor payments for accounts payable and receivable. In order to reduce overhead expenses, bookkeeping functions can also track assets, centralize general ledger data, and assess cost control. Employee records like vacation and sick days, employee spending, and training plans can all be tracked by human resource modules in addition to payroll. Orders from customers can be received and tracked, production schedules can be planned, items can be shipped, and stocks can be managed through production and planning modules.
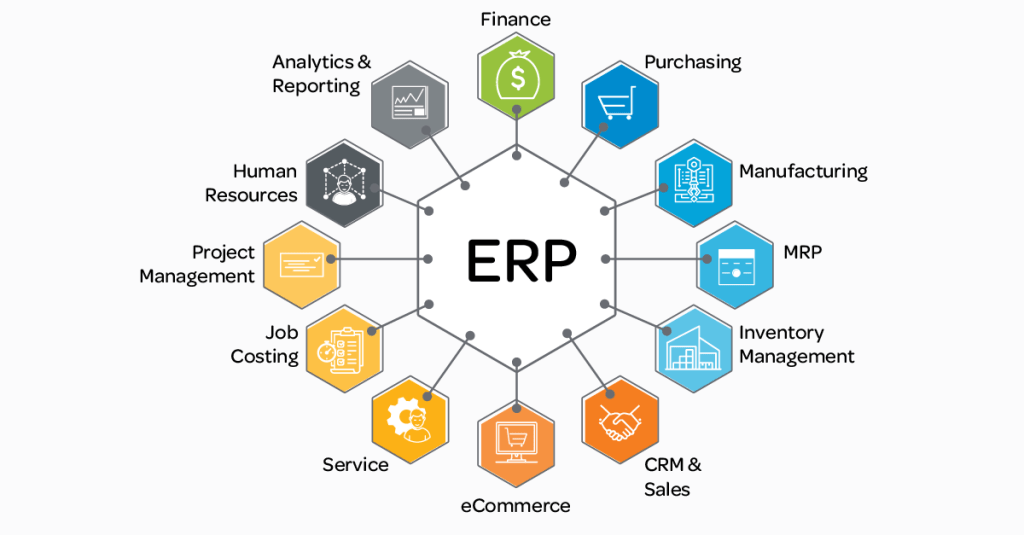
How we can use ERP
- Update our legacy systems.
- Cut down on inter-office paperwork.
- To standardize our manufacturing processes and increase productivity.
- Will give us more information and better access to our suppliers and customers.
Implementation
Steps for implementation of ERP in a firm:
- Cost analysis
- Blueprinting of Business Processes
- Staff Training
- Integration
- Data Conversion
- Going live with ERP
Summary:
- ERP is a business-wide common system.
- Can integrate all of our business units.
- Very expensive and time-intensive.
- Proper implementation can help the business function better.
- Poor implementation can hurt the business immensely.
- Training